C1.1 - Evolutionary Theory
Evolutionary Theory
Image of Tiktalik, fish-like organism found in Northern Canada

- All life forms are fundamentally similar at a cellular and molecular level
- Evolution explains life history on Earth
- Evolution is the process where organisms change over time
- evolution: theory that all species are descendants of ancient species differing from modern-day species
Theory vs. Hypothesis
- theory: set of statements that explain a group or phenonema
- hypothesis: suggested explanation of observations, that can be tested by further research or experiments
Early Theories
- Acceptance of evolutionary theory not universal
- Geological time not understood
- Archbishop James Ussher through the Bible, Torah, and other religious books researched age of Earth
- Ussher’s age of Earth: 4004 BCE — Earth is 6,000 years old
- Living things thought to be immutable (unchanging)
History of Geological Theories
- Humans are the only species to know their times are limited
- Driven humans to find an escape to death
- Religion offers time w/o end, place to go after death
- Christians are told they’re immortal, death is a phase
- Around 1650, James Ussher using religious books like the Bible, Genesis and the Torah determines beginning of time: 4004 BCE
- James Hutton challenged 6000-year-old history by looking at geological evidence
- i.e. the Grand Canyon in Arizona — Colorado river flows btwn. 2 states
- River digs canyon 1 ft. deep / 1000 years through erosion
- est. 5.5 million years to make canyon
- Erosion revealed layer of time, layer deposited 1 in. / 1000 yrs
- 6 in. of canyon = 6000 years
- Hutton realized that Earth is older than 5.5 million years
Theories Leading to Evolutionary Theory
Uniformitarianism — James Hutton
- uniformitarianism: theory that states the Earth was formed entirely through slow-moving processes like erosion and sedimentation, and that these processes continue to shape the Earth today
- Proposed by James Hutton, Scottish geologist
- Molten material is forced up to Earth’s surface to form rock
- Rock is then eroded away
- Sediment from erosion washed into the sea and eventually compacts to form sedimentary rock
- erosion: removal of surface material (i.e. rocks) through natural forces (i.e. water, wind)
- sedimentation: accumulation or depositon of sediments (small fragments) that compact to form a new structure
Principles of Geology — Charles Lyell
- Written by Charles Lyell, English geologist
- Popularized and expanded on Hutton’s theory of uniformitarianism
- Found more evidence to support that rocks were formed through slow-moving processes
Use and Disuse Theory — Jean-Baptiste Lamarck + adaptation
- adaptation: inherited characteristic that improves an organism’s ability to survive and reproduce in a particular environment
- Proposed by Jean-Baptiste Lamarck, French naturalist around the 1800s
GUIDING IDEAS
- By using or not using certain body parts, an organism develops certain traits
- i.e. giraffes developed long necks because they needed to reach food in tall trees
- inheritance of acquired characteristics: Enhanced developed characteristics will be passed down to that species’s offspring
- tendency toward perfection: Organisms continuously change and acquire features in order to be more successful in their environments
Theory Proven False
- Acquired characteristic would somehow have to change the DNA of specific genes in order to be inherited
- NO evidence of this happening
- Important in analyzing role of environment and explaining evolution as a process of environmental adaption
Histoire naturelle, générale et particulière — Georges-Louis Leclerc, count de Buffon
- Buffon did comprehensive work on natural history through his book Histoire naturelle, générale et particulière (1749-1804)
- Produced an account of the whole of nature
- First modern attempt to systematically present all existing knowledge on natural history, geology and anthropology in one book
Evidence
- Earth is old (~4 bil years old), made from destroyed stars
- Radiometric dating, caused by energy/particles being given off by nuclei (radiation)
- Akasta, NWT — 4 billion year old rock escaped being recycle
- Analysis of fossil record
- fossil: when bone or tissue turn into rock
- Leonardo DaVinci lived in Tuscany and walked in Italian moutain ranges
- Found seashell fossils in mountain ranges
- Evidence for tectonic plate movement — they push and make the land rise
- Vestigial organs: organs that had a use in the past but not anyomore
- i.e. goosebumps or appendix [questionable] in humans
- Comparative Development
- Embryology: study of development
- All vertabrates have a stage where pharyngenal pouches appear on the side of the throat
- Geographic distribution of species
- How did frogs get from Africa to South America if they die in salt water?
- Chromosomal analysis
- Chimpansees have 47 chromosones while we have 46
- Molecular analysis and biology
- Chemical processes of cells are similar or the same
- Amino acids that differ in human and gorilla hemoglobin is only 1 in a chain of 146 acids
Specific Examples
- Changes in Beak Shape
- In medium ground finches, beak size increases during dry years
- In “wet” years, beak size decreases for abundant vegetation
- Antibiotic Resistance in Bacteria
- Tubercolosis (TB) bacteria was treated using an antibiotic (drug) called Streptomycin, developed in the 1940s
- 1970s: TB almost completely wiped out
- 2006: Outbreak of extremely resistant strain of TB in KwaZulu-Natal, South Africa
- 2009: WHO reports that 1/3 of world population has TB
- Some TB bacteria developed resistance to their antibiotics and they survived
- These antibiotic-resistant bacteria reproduced and spread
Geographic Distribution of Species
Closely Related but Different
- Finches that Darwin found were all descendants of a single ancestral species from South American mainland
- Finches became geographically isolated and developed characteristics best suited for their particular environment
- i.e. beak shape and size
Distantly Related but Similar
Similar selection pressures of species in geographically diff. areas forced them to develop similar traits
Fossil Record
Image of a fossil
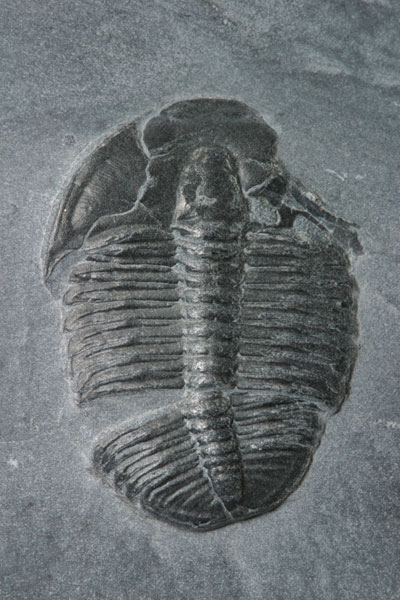
- fossil: preserved remains of organisms turned into minerals
- Organisms die and become trapped in sediments
- Fossilization is very rare; requires water and no disturbance
- Fossil record is incomplete
Types of Fossils
- body fossil: fossil that preserves the remains of a former organism
- molds: imprint left by remains of organism in rock/clay
- external mold: mold outside of remains
- internal mold: mold inside of remains
- cast fossil: replica of an organism formed by molds
- trace fossil: fossil that preserves the activities of a former organism
- i.e. dinosaur footprints, ancient worm burrows
Palaeontology — Georges Cuvier
- palaeontology: study of fossils
- Shallower depositos reveal organisms most similar to those alive today
- Relative age of fossils determined by French zoologist Georges Cuvier
- Wrote Tableau élémentaire de l’histoire naturelle des animaux in 1797
- Leçons d’anatomie comparée (1800-05)
- Disagreed w/ viewpoints of Lamarck
- Catastrophism responsible for extinction events
Radioactive Decay
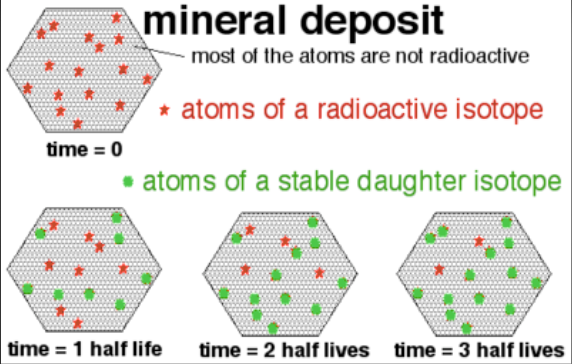
- Allows absolute age of rock to be determined
- Ratiometric dating used to measure amount of daughter isotope in sample
- Decay constant over time
- Carbon-14 testing used for more recent organic remains
Beginnings of Evolutionary Thinking
- James Hutton proposes that geological change occurs over long period of time
- Charles Lyell writes Principles of Geology
- uniformitarianism states that Earth continues to change through gradual, uniform processes
Sources
- Mr. C. Jones
- BiologySource 11
- https://www.britannica.com/science/erosion-geology
- https://www.britannica.com/science/erosion-geology
- https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=9pDaBQnFLTM
- https://www.britannica.com/biography/Georges-Cuvier
- https://www.britannica.com/biography/Georges-Louis-Leclerc-comte-de-Buffon
- https://samnoblemuseum.ou.edu/common-fossils-of-oklahoma/how-to-become-a-fossil/different-kinds-of-fossils/