C1.3 - Genetic Variation and Microevolution
Modern Synthesis
Image of Chromosomes of DNA
- Darwin had no concept of actual mechanism of inheritance
- Genetics later integrated into evolutionary theory
- Called “modern synthesis”
- Organisms vary in # of genes
- Sexual reproduction increases variation
- Variation is a good thing, species more resistant to changes / diseases
Microevolution and Macroevolution
- microevolution: evolutionary changes that occur within a species
- macroevolution: evolutionary changes that result in a new species forming
Mutation
- Source of new alleles
- allele: genetic trait
- May be neutral, harmful or beneficial
- Affects fitness of individual
- Harmful mutations usually result in death of gamete
- gamete: sex cell / sperm or egg
Gene Pool and Variation
- gene pool: the “reservoir” (current gen.) from which future generations draw their genes from
- Sources of Varaition: mutations and sexual selection
- Hardy-Weingberg Equilibrium: populations that do not undergo changes to their gene pools — 5 conditions:
- random mating
- large population
- no movement in and out of population
- no mutations
- no natural selection
Genetic Drift (Mechanism of Microevolution)
- genetic drift: changes to genetics in small populations
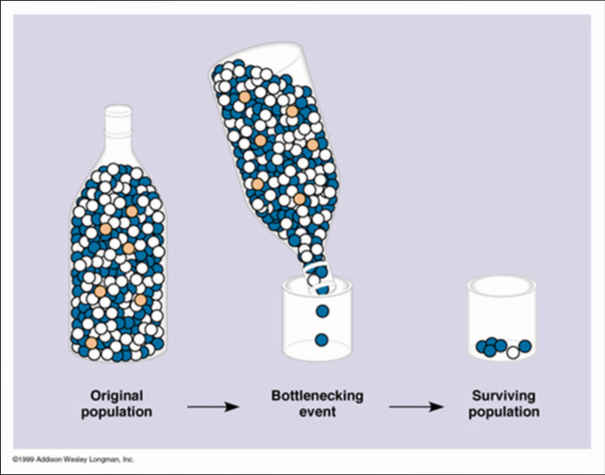
- bottleneck effect: catastrophe that dramatically reduces a population
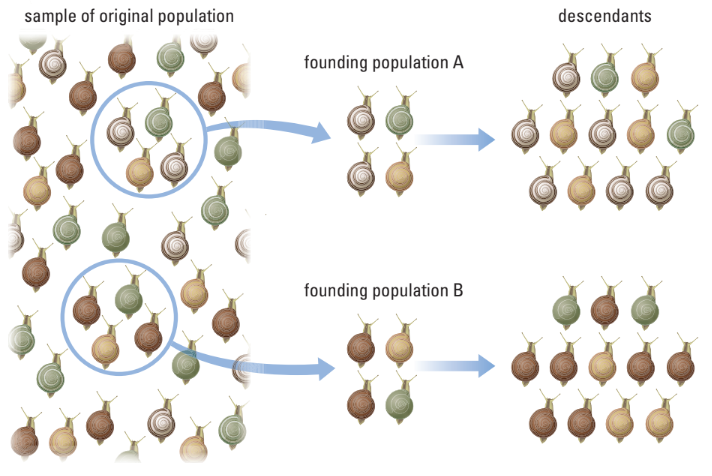
- founder effect: individuals leaving a population to establish a new one
- Genes flow between populations during migration
Bottleneck Effect
Founder Effect
Phenotypes and Effects of Selection
Variations / phenotypes of wild mustard
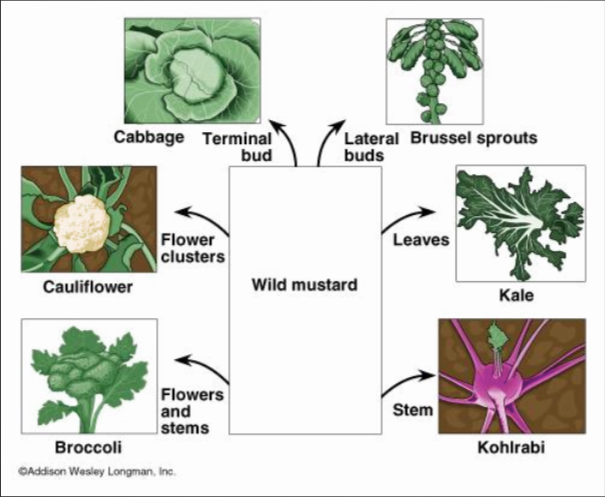
- phenotype: how organism (traits) appear
- Mutations provide variations in traits selected by outside influences
- Natural selection acts on individual phenotypes that are passed on to subsequent generations
- Variable environments favour multiple phenotypes
Types of Selection — Mechanisms of Microevolution
Bell Curves
bell curve: frequency compared to any variable
Bell Curves of Selection
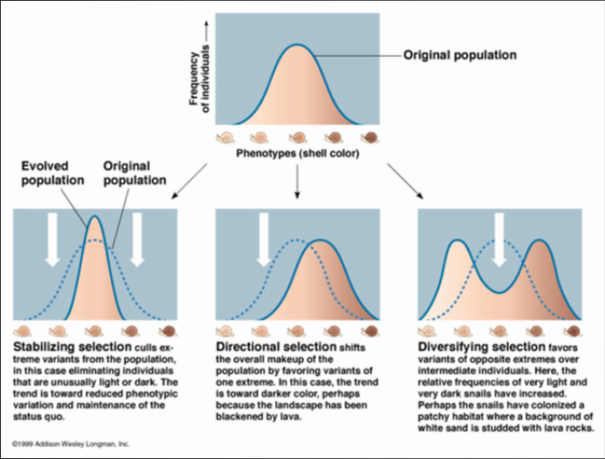
Stabilizing Selection
- stabilizing selection: selection against individuals exhibiting variation in a trait that deviates from the current average
- Most common form of selection
- Phenotype extremes are select against
- i.e. human birth weights
- Small babies have less fat (more cold) and take longer to breastfeed
- Big babies have trouble coming out
- Humans have trouble coming out of womb than quadropeds (4-legged)
- Mother has small pelvis and the head has to go out first
Directional Selection
Direction selection of dark phenotype of peppered moth during industrial revolution

Peppered moth used to be lighter in colour, but shifted to darker colours after industrial revolution started polluting the environment with coal dust.
- directional selection: selection that favours an increase or decrease in a phenotypic trait
- Follows dramatic change in environment
- i.e. migration, climate change, pollution
- Individuals at one extreme are more successful in future generations
Pesticide Resistance
- A lot of bugs that eat our crops are killed using pesticides (bottleneck event)
- Some bugs however have a mutation making them resistant to the pesticide
- These mutated bugs reproduce and grow
- Pesticide is no longer effective
Disruptive Selection
- disruptive selection: selection that favours 2+ variations that differs from the population average
- Usually at the 2 extremes of a trait
- Environmental change produces two distinct food sources
- i.e. hummingbird bill length
- 1 species hummingbird in Ontario
- 2 species hummingbird in Canada
- some hummingbirds prioritize short flower tubes and others prioritize long flower tubes
- the average struggles at either
Other Mechanisms of Microevolution
- sexual selection
- genetic drift
- artificial selection
- gene flow: exchange of genes w/ another population
Types of Selection, Part II
Reproduction Terminology
- polygamy: dominate male w/ subordinate females (common)
- polyandry: dominate female w/ subordinate males (rare)
- monogamy: paried relationships
- i.e. Royal Albatross, partners take turns w/ responsibilities and taking care of children
- sexual dimorphism: physical differences between sexes
Sexual Selection — Mechanicsm of Microevolution
- sexual selection: selection that favours any trait that most partners deem valuable
- Continued selection resulted in sexual dimorphism
- Female mates best choice from male competition
- i.e. peacock tails, fiddler crab claws
- Females have the most to lose from a bad mate
- Have to raise a child w/ less favourable genes
Cumulative Selection
- “The blind watchmaker” theory: Complex structures are so complex that if one structure is removed, whole structure breaks. That means an “invisible maker” had to have designed these structures.
- evolutionary theory has more evidence
- cumulative selection: evolution of complex features
- Mutations are result of chance, natural selection is not
- Accumulation of favourable mutations result in complex structures like the eye
Evolution of the Eye
- At the beginning, eyes could only detect brightness of light
- Over time, more complex structures formed
- Pinhole formed to focus light
- Pinhole gets covered by translucent/transparent structures that acts as a lens
- Muscles formed in eye to focus lens on desired object
Adaptation of Existing Structures into New Ones
- Existing structures are repurposed to fulfill different tasks
- i.e. exoskeleton of a reef lobster protects from predators…
- … but exoskeleton of scorpion helps it resist water loss and support itself on dry land
- i.e. penguins use their wings not to fly, but to swim rapidly in water
Altruism
- altruism: selfless concern for the well-being of others
- One organism benefits from another’s behaviour to their detriment
- detriment: to lose smth.
- Species help other species because they indirectly pass their genes on
- Better treatment to others returns back to improve the fitness of an animal group as a whole
- Examples of altruism
- insect colonies like bees
- birds
- monkeys (grooming)
- humans
- Kin selection increases chance of genes being passed on
Sources
- Mr. C. Jones
- BiologySource 11
- https://www.britannica.com/animal/peppered-moth
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Altruism
- https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=4SXHMm5I-68