C3.1 - Internal Systems and Regulation
Organ Systems
- Human body cells arranged in a hierarchy
- tissue: group of specialized cells that work together to perform a specific task
- organ: structure composed of different tissues specialized to carry out a specific function
- organ system: group of organs that have related functions
flowchart TD
a["`**Specialized Cells**
(i.e. cardiac muscle cells)`"] --> b
b["`**Tissues**
(i.e. cardiac tissue)`"] --> c
c["`**Organ**
(i.e. heart)`"] --> d
d["`**Organ System**
(i.e. circulatory system)`"]
Human Organ Systems
mindmap
[Human Organ Systems]
(Digestive)
(Circulatory)
(Respiratory)
(Reproductive)
(Excretory)
(Locomotion)
(Endocrine, horm.)
(Nervous)
4 Types of Tissue
- epithelial tissue forms protective structures in body
- lines outer layer of skin and many organs
- form glands in body to produce hormones, enzymes, and sweat
- connective tissue supports and protects structures in the body
- also connects two structures together
- found in
- tendons (connect muscle to bone)
- ligaments (connect bone to bone)
- bones
- cartilage (stops bones from rubbing on each other)
- blood
- fat
- muscle tissue allows for movement in body
- skeletal muscle: muscle located in arms, legs, and areas with bones to help us move
- smooth muscle: muscle located in digestive tract to help food move through the digestive system
- cardiac muscle: muscle located in the heart to help the heart move to pump blood
- smooth and cardiac muscles allow the organs to move
- nervous tissue responds to stimuli and sends signals throughout body
- stimuli: factor that causes the body to react to it —> change of bodily activities
- found in brain, spinal cord, nerves
Respiration and Gas Exchange
- Essential for all organisms
- Oxygen in → carbon dioxide out
- Different organisms have different gas exchange systems
- All rely on moist respiratory surfaces
- breathing: ventilation of respiratory system with air
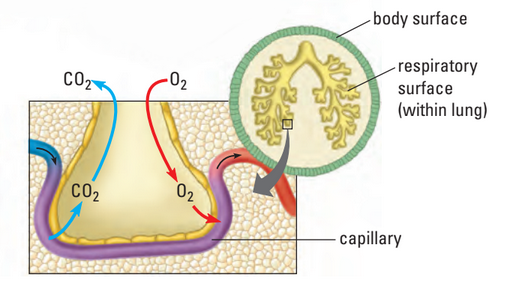
Respiratory Surfaces
- respiratory surface: special, moist membrane where gas exchange occurs
- cellular respiration: process that produces energy needed to fuel all cell activities
- glucose + oxygen → water + carbon dioxide + ATP
- Characteristics of Respiratory Surface
- very thin and moist → permeable to gases being diffused
- large surface area to maximize diffusion
- diffusion gradient must be maintained
- diffusion: high conc. → low conc.
- relative difference in concentration of oxygen and carbon dioxide in both sides required
Membrane Diffusion Only
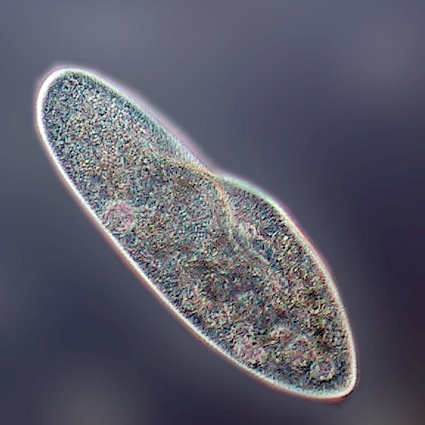
- Found in single-celled and some multi-celled organisms
- Rely on simple diffusion
- Concentration gradient
- high concentration → low concentration
- i.e. bacteria, protists, flatworms, hydra
Specialized Respiratory Systems
- Larger organisms require more complex respiratory systems
- Simple diffusion effective only to thickness of few cells
- Systems include:
- respiratory surface
- passageways
- muscular structures associated w/ respiratory surfaces
I. Skin Respiration

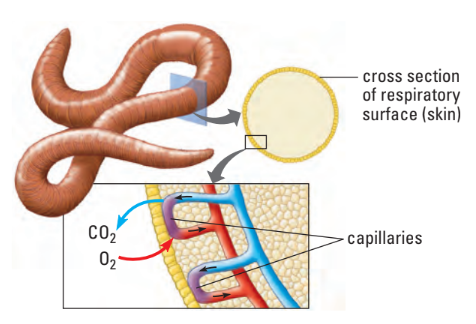
- Moist surface
- Tissue lined w/ capillaries
- Occurs across all of body surface
- Species relying on skin respiration generally small or have flat bodies to have large surface area
- i.e. earthworms
II. Gills

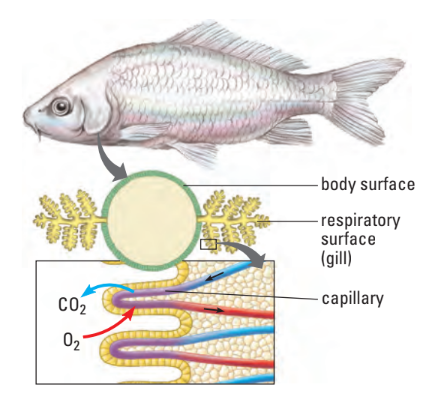
- gills: folds in the body surface specialized for gas exchange
- feathery tissues in aquatic animals
- high surface area
- ventilated w/ oxygen-rich water
- enables water to flow so that gases can diffuse from water and across respiratory membranes
- may be combined w/ other functions like feeding (bivalves) and locomotion (octopus)
- i.e. fish
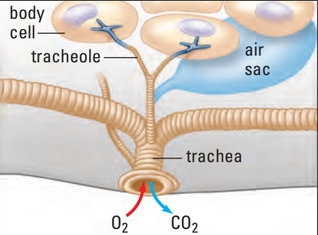
III. Tracheal Respiration

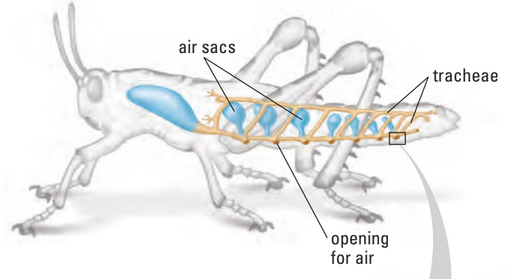
- tracheal system: system of tubes that extend through their bodies
- tracheae: larger entry tubes
- tracheoles: smaller branching tubes from tracheae
- Internal system in insects
- Open to exterior by spiracles
- spiracle: valved pores used for breathing
- Internal network of tracheae
- Ventilated through muscular contractions
- Generally, insects don’t need circulatory system for gas exchange (diffusion enough)
- Larger insects sometimes pump in more air through rhythmic body movements
- … compressing and expanding the air
- i.e. grasshopper
IV. Lungs
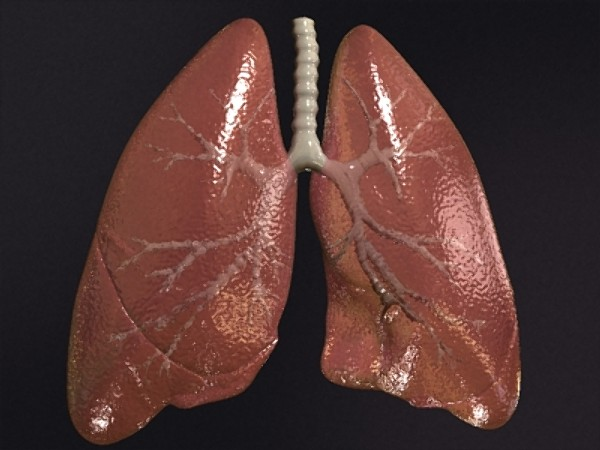
- lungs: internal, thin-walled sacs with a large surface area
- Internal structures connected to exterior by specialized passageways
- 3 components
- lungs w/ moist respiratory system
- circulatory system
- ventilation system
- i.e. terrestrial vertebrates, arachnids (book lungs)
- Inside lungs, oxygen gas diffuses into blood and is transported via vessels across body
- Carbon dioxide diffuses out of blood, enters lungs, and moved out









