C3.10 - Mammalian Heart
About the Heart
- Pumps blood through 160,000 km of blood vessels
- Beats 90k times / day, every day throughout person’s lifetime
- Heartbeat consists of…
- systole: rhythmic contraction
- diastole: relaxation of myocardium
- myocardium: entire cardiac muscle
Cardiac Cycle
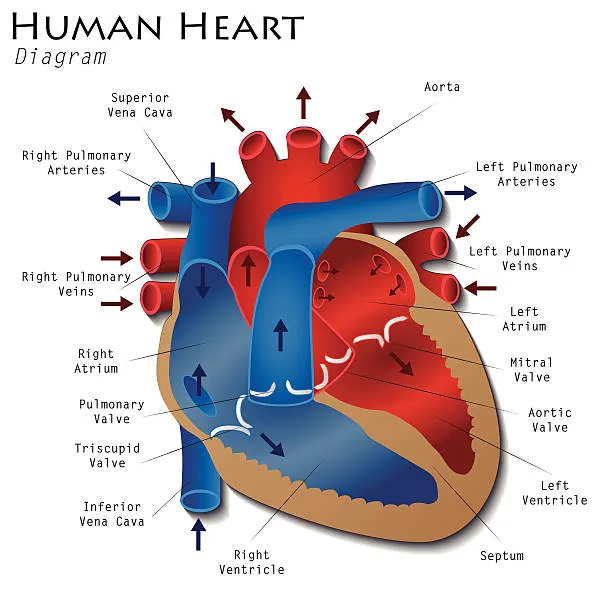
- 4-chambered heart: L/R atria and ventricles
- atria: receive blood from veins and pumps them into ventricles
- ventricle: receive blood from atria and pumps them away from heart
- Two atria contract simultaneously
- little pressure generated
- Two ventricles contract simultaneously shortly after
- high pressure generated
- mitral / bicuspid valve: two-part valve that separates left atrium and l. ventricle
- tricuspid valve: 3-part valve that separates right atrium and r. ventricle
- atrioventricular valves: valves located between atria and ventricles
- two valves listed above
- soft “lub” sound
- semilunar valves: 2 valves that prevent blood flowing back from…
- r. ventricle and pulmonary artery
- l. ventricle and aorta
- louder “dub” sound
- pulmonary valve between r. ventricle and pulmonary art.
- aortic valve: between l. ventricle and aorta
- Deoxygenated blood from body collected by superior and inferior vena cava
- R. atrium contracts pumping blood to r. ventricle
- R. ventricle contracts and pumps blood to lungs through pulmonary artery
- Oxygenated blood in pulmonary veins returns to heart via l. atrium
- L. atrium contracts and sends oxygenated blood to l. ventricle
- L. ventricle contracts and pumps blood out through aorta
2 Circuits of Bloodflow
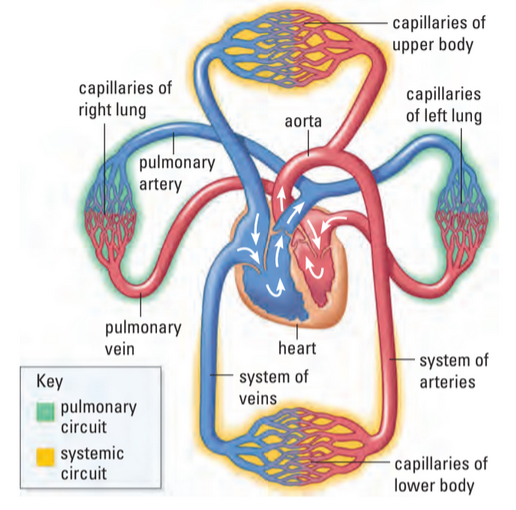
Pulmonary Circuit
pulmonary circuit: pathway of blood where blood travels from R. side of heart to lungs
R. atrium → R. ventricle → pulmonary artery → lungs → pulmonary vein → l. atrium
Here, artery has deox. blood and vein has ox. blood
Systemic Circuit
- systemic circuit: pathway of blood where blood is pumped through aorta
- aorta: artery that supplies oxygen to all body systems
- superior vena cava: vein entering heart from upper body
- inferior vena cava: vein entering heart from lower body
L. atrium → l. ventricle → aorta → body → vena cava → r. atrium
Blood Supply for Heart
coronary arteries: pair of arteries branching from the aorta to supply heart muscle with necessary nutrients
Control of Heartbeat
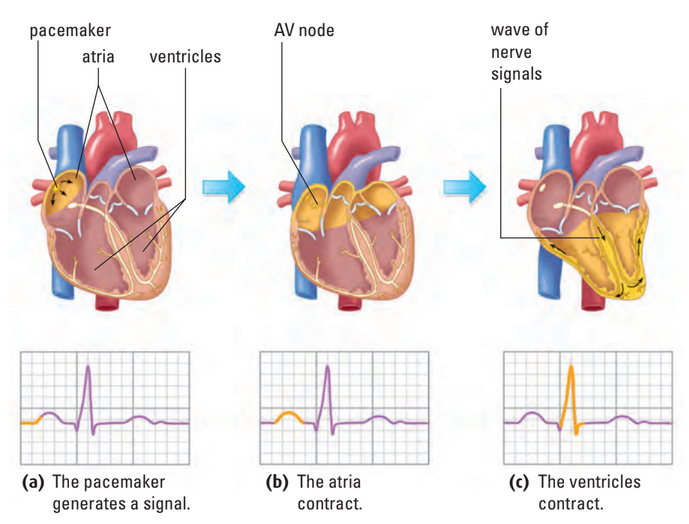
- Heart continues to beat when body is asleep / unconscious
- Heartbeat self-regulated
- sinoatrial (S-A) node: natural “pacemaker” of heart
- originates in bundle of fibres in r. atrium
- fires and contracts atria
- controlled by both nervous and endocrine system
- hormones: chemical messengers of the body
- Impulse / cardiac action potential spreads to atrioventricular (A-V) node
- Ventricles contract
- Bundle of His and Perkinje fibres aid in spread of cardiac action potentials
Electrocardiograms (ECGs)
Parts of an ECG
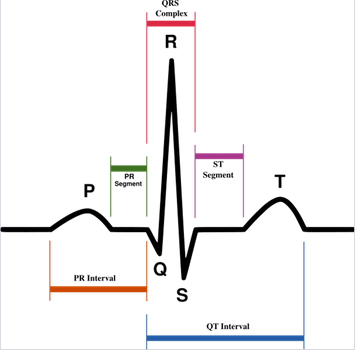
- electrocardiodiagram (ECG / EKG): graph that measures change in voltage between electrical signals of “pacemaker”
- : contraction of atria
- to : contraction of ventricles, repolarization of atria (immeasurable)
- : repolarization of ventricles before next firing
- Random contractions of heart cause fibrillation
- defibrillator: device that applies strong electrical current to heart which may reset the pacemaker
- WILL NOT start a stopped heart
- Noradrenaline causes SA node to fire more rapidly
- Acetylcholine slows SA node firing
- Both released through impulses gen. in medulla oblongata
Defibrillator
Sources
https://www.istockphoto.com/vector/human-heart-diagram-gm477331500-66758051