C3.11 - Circulation and Homeostasis
Homeostasis
- homeostasis: state of internal stability maintained by body
- normal pH state of blood
- goal of circulatory system
Hypertension
- hypertension: high blood pressure
- Occurs when BP > 140/90 for ext. period of time
- Increases risk of heart disease
- Diets high in salt and cholesterol increase BP
- BP increases with:
- age
- lack of exercise
- obesity
- certain ethnicities
- African
- Aboriginal
- South Asian
- stress
- excess alcohol
- smoking
- High cholesterol diets may lead to arteriosclerosis
- arteriosclerosis: disease where plaques are deposited in arteries
- leads to obstructions
- ⚠ possible heart attacks
- see more in Disorders
Blood Pressure (BP)
Device to measure BP
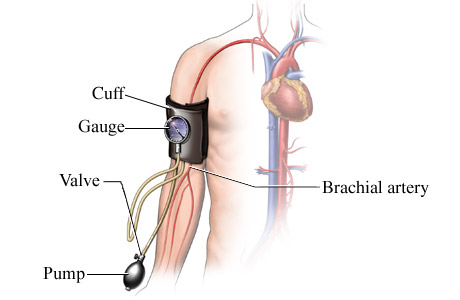
- BP and heart rate increase from increased O2 demand
- systolic pressure: highest pressure resulting from contraction of l. ventricle
- diastolic pressure: lowest pressure before another ventricular contraction
- sphygmomanometer: pressure cuff used to measure blood pressure
- average: 120/80 mm Hg (120 systolic / 80 diastolic)
Lymphatic System
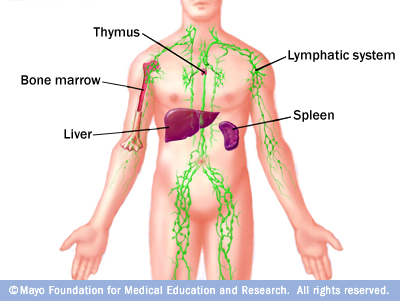
- Vascular transport system incl. spleen
- Network of glands and valved vessels
- Contains lymph
- usually clear, colourless, oily fluid
- Helps maintain fluid balance in mammals
- Collects blood plasma that has leaked out of capillaries
- interstitial fluid: leaked plasma
- Lymph returned to blood stream through ducts opening onto l. and r. subclavian veins
- Flow of lymph dictated by movement of gut and skeletal muscle
- Involved in immune response
- Lymphocytes produced in lymph nodes
- Lymph glands swell when body fights infection
Lymphatic System — PART II
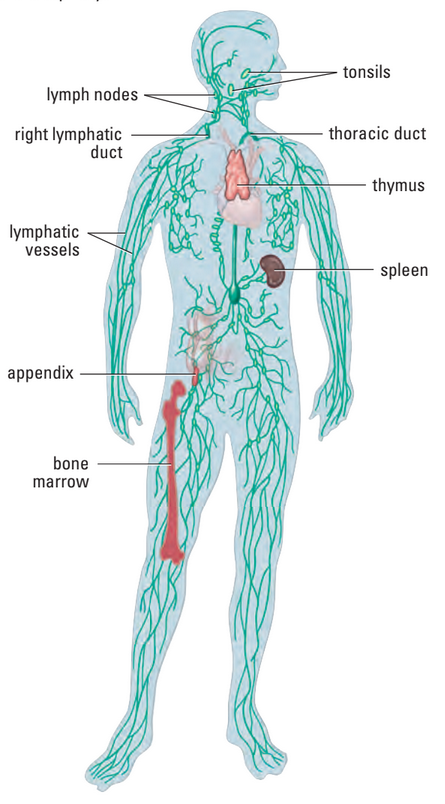
- ~3-4 L of fluid / day leave blood to surround your cells
- lymphatic system: organ system that collects fluid leaving capillaries
- screens them for microorganisms
- then returns them to the circ. system
- lymph: fluid leaked out of circ. system, collected by lymphatic vessels
- clear, watery fluid made up of
- protein molecules
- salt
- gluocose
- others
- clear, watery fluid made up of
- Lymph collects in system of lymph vessels
- Have valves to prevent lymph from flowing back toward capillaries
- Muscle contractions + vessel squeezing + valves → help move lymph
- Eventually drains into circ. system near heart
- spleen: organ that helps remove old / damaged blood cells, stores platelets and
- helps control amount of blood and blood cells in body
- Lymph vessels alongside small intest. pick up fats and fat-soluble vits. and transports to blood
- Helps provide immunity
- thymus: organ where WBCs mature
- lymph node: small, bean-shaped enlargements that filter out harmful organisms and abnormal cells
Temperature Regulation
- homeotherm: body temp. does not fluctuate
- i.e. lion
- poikilotherm: body temp. fluctuates according to environ. factors
- i.e. tortoise
- Body temp. of 37.5 °C maintained via behavioural and physiological mechanisms
- Ex. behavioural
- sitting in shade
- putting on clothing
- Ex. physiological
- Heat loss from skin surface regulated by…
- vasoconstriction; or
- vasodilation of blood vessels
- countercurrent heat exchange system in arms and legs
- Heat loss from skin surface regulated by…
- Ex. behavioural
Health of Circulatory System
Plaque
plaque: patchwork of cholesterol, calcium, and fat deposits that stick to interior vessel walls
Dangers
- atherosclerosis: narrowing of arteries resulting from plaque buildup
- pathway narrows → BP increases
- angina pectoris: chest pains felt from partial blockages
- occurs when deposits on artery wall harden
- weakens arterial elasticity
- heart attack: stoppage / severe slowdown of blood supply to heart tissue
- majority cause: atherosclerosis
- sudden cardiac arrest: heart suddenly stops functioning
- most common cause: coronary heart disease
Disorders
- arrhythmia: heart beats irregularly (too slow, too quick)
- hypertension
- above
- heart failure: condition where heart cannot pump blood efficiently
- because it can’t fill with enough blood
- or send blood w/ enough force
- aneurysm: bulge in wall of artery
- stroke: blood clot forming in artery going to brain
Choices Helping Cardiovascular Health
- Foods high in fiber
- Low in salt and cholesterol
- cholesterol: fat part of cell membranes used to synthesize hormones, bile, and vit. D
- made by liver
- high-density lipoprotein (HDL)
- “good cholesterol”
- removes excess cholesterol from tissues and arteries
- low-density lipoprotein (LDL)
- “bad cholesterol”
- becomes part of plaque in arteries
- Maintain healthy weight
- Exercise regularly
- Avoid smoking and inhaling smoke
- Regular health check ups