C3.2 - Mammalian Respiration
Respiration
- All mammals share the same basic respiratory structure
- Respiration subdivided into 3 activities
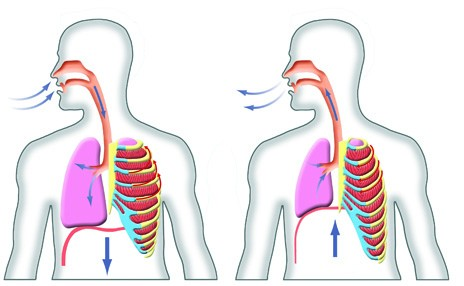
- Breathing: inspiration / inhalation (air in) [L] and exhalation / expiration (air out) [R]
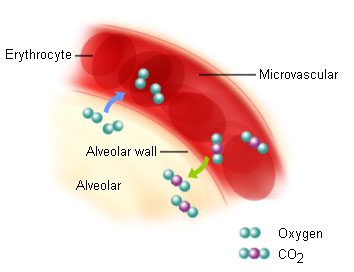
- External Respiration: exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide between air and blood
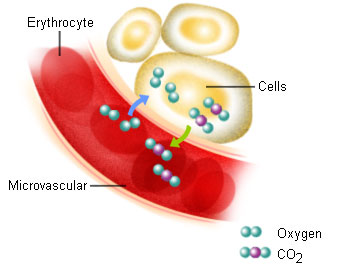
- Internal Respiration: exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide between blood and cells of surrounding tissue
- Breathing: inspiration / inhalation (air in) [L] and exhalation / expiration (air out) [R]
Respiratory Tract (RT)
- respiratory tract: the passageway of which air passes through the body
- Lungs protected deep within body
- Connected to exterior by passageways
Path of Oxygen in RT (Diagram)
flowchart TD air[**AIR**] --> a a[**Nose / Mouth** Filtered by nasal hair/mucus Warmed and moistened] --> b b[**Pharynx** Epiglottis blocks food to trachea] --> c c[**Larynx** Vocal cords in here vibrate to make sounds] --> d d[**Trachea** Held up by cartilageous rings] --> e e[**Bronchi**] -- ***To Lungs*** --> f f[**Bronchioles**] --> g[**Alveoli**]
The Upper RT
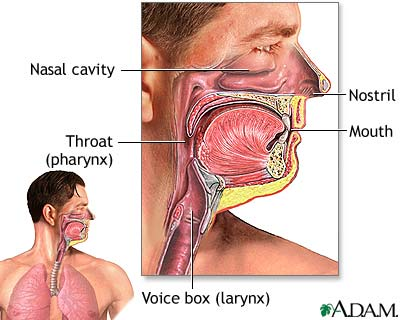
- Air enters nostrils (nares) or mouth
- Air is warmed and moistened by hair and mucus in nose
- Air passes through pharynx, glottis, and larynx
- pharynx: junction of esophagus, trachea, nasal cavity, and larynx
- esophagus: passageway to stomach
- glottis: opening of trachea
- trachea (windpipe): flexible passageway to lungs, supported by cartilaginous rings
- epiglottis: flap preventing food and liquids passing into the trachea
- larynx: voice box housing vocal chords
- cilia: microscopic hairs in the body
- Upper RT line w/ cilia that continually pass foreign particles, fluids, and debris up and out of RT
The Lower RT
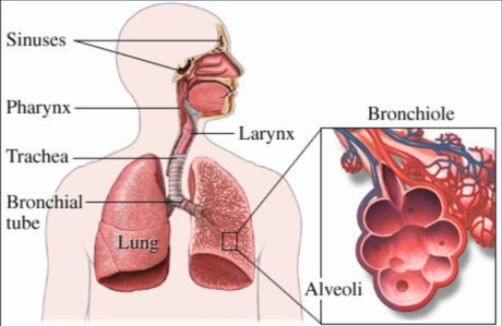
- Trachea branches into 2 bronchi, one for each lung
- Lungs divided into lobes:
- 3 on right
- 2 on left
- Bronchi then branch into many bronchioles
- Bronchioles end in grape-like clusters of alveoli
RT Lining
- Lined with moist epithelial tissue (from 4 types of tissue)
- Epithelial tissue covered with cilia and fine layer of mucus in trachea and bronchi
- Mucus traps foreign particles and removes them from air
- Cilia sweep mucus-trapped particles up to pharynx for disposal or swallowing
Alveoli
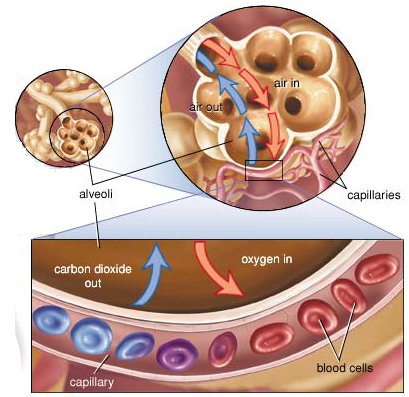
- alveoli: sacs in lungs where gas exchange takes place
- One cell thick
- Closely associated w/ capillary networks
- Blood takes up oxygen through simple and facilitated diffusion
- Alveoli coated in surfactant to reduce surface tension
- Inner surface of each alveolus lined with layer of moist epithelial cells
- Oxygen in air dissolves in film of moisture on these epithelial cells
- Oxygen diffuses into capillaries and binds to hemoglobin on RBCs
- Hemoglobin increases efficiency by creating diffusion gradient
- RBCs transport oxygen throughout the body