C3.4 - Control and Regulation of Respiration
Control of Breathing
- Conscious control for short periods
- i.e. holding breath underwater
- Concentration of carbon dioxide in body predominately determines breathing rate
- when CO2 dissolves in water, it forms carbonic acid
- rich blood reaches the medulla oblongata at the base of the brain
- medulla oblongata: part of brain that sends out nerve impulses to muscles of rib cage and diaphragm to control breathing
- Minor factors in control
- concentration of oxygen in carotid artery and aorta
- blood pH
- lung capacity
- homeostasis: state of internal stability maintained by body
- normal pH state of blood
Breathing at High Altitudes
- High altitudes: Lower air pressure, proportionally less air than lower altitudes
- Air is thinner or rarified
- Less oxygen available for respiration
- Altitude sickness or hypoxia may result
- Symptoms
- high breathing rate
- decrease in blood pH
- increase in pulmonary blood pressure
- pulmonary edema
- Short-term adaptions to altitude
- increased breathing rate
- increased production of RBCs (increased hematocrit)
- Long-term genetic adaptations
- short build, short limbs
- large lung volume
- high pulmonary blood pressure
- more alveoli in lungs
Diving

Elephant seal
- Elephant seals dive 400 m, 40 atm. for over 20 mins.
- Sperm whales capable of staying in 2 km depths for >1 h
- Animals experience hypoxia but utilize oxygen stores throughout body
- Heart rate slows (diving bradycaria)
- Blood flow diverted to brain and heart
Respiratory Impairment
- Respiratory system no longer able to adjust to environmental conditions
- Drowning
- laryngospasm: larynx closes and person asphyxiates
- fresh water drowning: alveoli collapse, gas exchange ends
- salt water drowning: fluid drawn out from lungs, oxygen can’t reach alveoli walls
- Carbon monoxide poisoning
- CO binds to oxygen receptors of hemoglobin w/ more affinity
- Results in suffocation
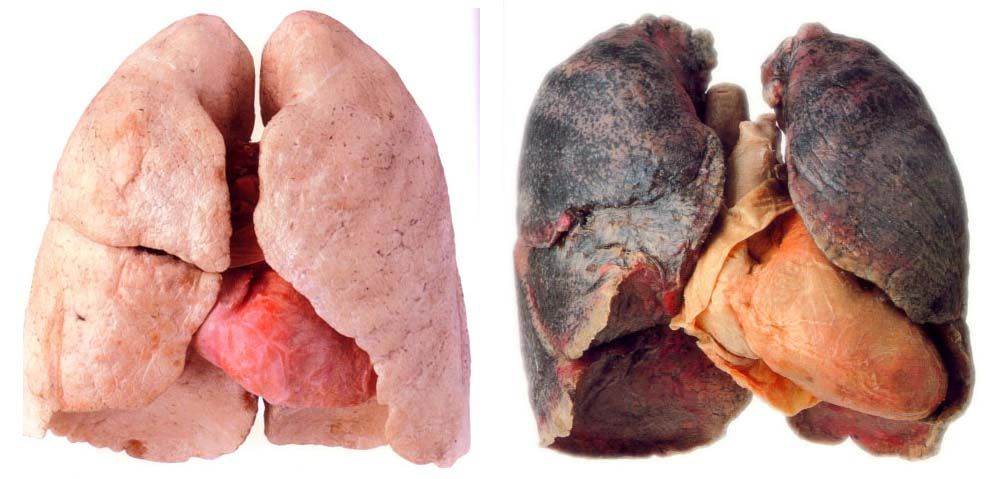
- Smoking
- Cilia in trachea paralyzed or killed
- Mild CO poisoning
- Smoke particles lodged in respiratory pathways
- Tar coats lungs, alveoli become brittle
- Consequences
- coughing, snoring
- CO poisoning, lung cancer, emphysema
- Air pollution
- varied forms
- contributes to asthma, smog
- Diabetes affects your breathing
Common Disorders
- sinusitis: condition where sinuses become swollen and irritated
- caused by virus and bacteria
- sinus: moist air space around nose
- symptoms: stuffy / runny nose, pain / swelling around eyes and cheekbones, pressure in head
- influenza: common viral infection of upper respiratory system
- spread by airborne droplets and contact w/ contaminated objects
- can develop into pneumonia in more serious cases
- pneumonia: infection of lungs where alveoli in lungs fill with fluid, preventing oxygen from reaching blood
- caused by variety of
- viruses
- bacteria
- fungi
- parasites
- caused by variety of
Other Disorders
- asthma: chronic disorder where airways become narrowed
- when smooth muscles contract in bronchi and bronchioles
- airway becomes narrow
- breathing becomes difficult
- can be life-threatening
- may be caused by air pollution, cold air, smoke, drugs, and infections
- bronchodilator: drug that causes narrowed airways to expand, delivered often by puffer
- bronchitis: infection of bronchioles or airways connecting alveoli and trachea
- produce excess mucus
- may cause frequent coughing and difficulty breathing
- may be chronic when exposed to smoke or pollution
- emphysema: “over-inflated lungs”
- occurs when cilia in airways are damaged
- bronchioles become clogged → less air to alveoli
- air pressure builds up and eventually tear alveoli walls up
- increased heart and breath rate
- causes: smoking, exposure to chem. hazards (mines)
- chronic obstructive pulmonary disesase (COPD): serious condition combining chronic bronchitis and emphysema
- usually requires external source of oxygen
- cystic fibrosis: fatal genetic disease where abnormally thick mucus blocks airways
- traps bacteria in lungs and leads to lung tissue infection
- severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS): serious pneumonia-like respiratory disease caused by a coronavirus
- coronavirus spread through coughing / sneezing
- Lung Cancer
- tumour: groups of cancer cells
- cells in lungs reproduce too quickly
- 85% of cancers linked to smoking
Normal Lung (left) vs. Smoker’s Lung (right)