C3.7 - Choosing a Healthy Diet
Healthy Diet
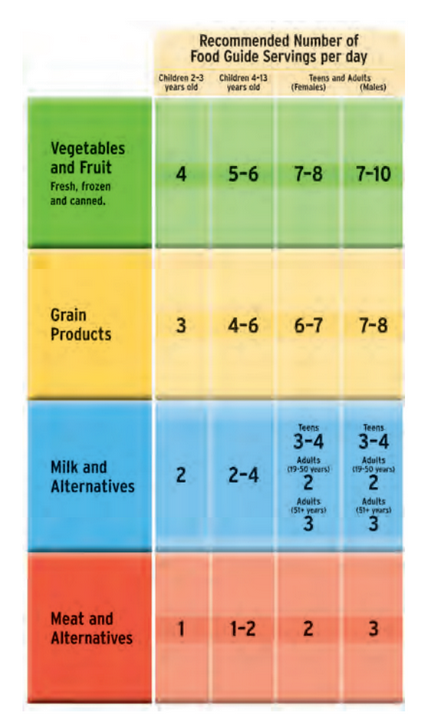
- Canada’s Food Guide to Healthy Eating
- Contains food groups that will provide all daily nutritional requirements
- 1 serving size equal to
- medium fruit
- 125 mL vegetables
- half bagel / small waffle
- 200 mL milk / yogurt
- 30 mL peanut
- 75 g chicken
Nutrients
Carbohydrates
- carbohydrates: compounds made up of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen
- major source of energy for humans
- can be used directly or be stored
- 2 types
- Simple Carbohydrates (i.e. sugars → fruit, honey, milk)
- Complex Carbohydrates (i.e. starches → bread, rice, potatoes)
- glucose: main fuel supply for cells
- used for cellular respiration
- or for making larger carbs / fat molecules
- glycogen: chain of many glucose molecules
- cellulose / fibre: complex carbohydrate often found in fruits and vegetables
Proteins
- protein: complex molecule constructed from 20 kinds of amino acids
- amino acid: organic molecules that compose a protein
- Contribute to almost all day-to-day functions
- i.e. form hair muscles
- long-term nutrient storage
- may defend against harmful microorganisms
- facilitate inter-cell communication
- enzyme: protein that speed up specific chemical reactions without being consumed
- essential amino acids: 1 of 8 amino acids that our cells cannot make from other molecules
Fats
- fats / lipids: molecules formed from fatty acids and glycerol
- store energy in body and help body absorb fat-soluble vitamins
- provide body with insulation
- saturated fats: fats with single bonds between carbon atoms in fatty acids
- has max. number of hydrogen atoms
- high intake promotes buildup of fat deposits within blood vessel walls
- unsaturated fats: fats with at least one double bond in a fatty acid chain
- found in
- fruits
- vegetables
- nuts
- seeds
- fish
- olive / sunflower seed oil
- important part of healthy diet
- trans fat: partially hydrogenated unsaturated fat (processed to accept more hydrogen atoms)
- solid at room temp.
- longer shelf life than other unsaturated fats
- often used in fast food
- contribute to heart disease and bad health
Vitamins and Minerals
- vitamin: organic nutrient needed in small amounts to regulate body processes and perform chem. reactions
- organic nutrient: nutrient that contains carbon
- Types of Vitamins
- water-soluble cannot be stored in body, continuous intake required
- fat-soluble be stored in fatty tissue in small amounts
- mineral: inorganic nutrient that don’t contain carbon
- important minerals: Ca, Fe, P, Cu, Na, Zn
- Found naturally in foods like
- meat
- eggs
- dairy
- whole-grain products
- tofu
- green leafy vegetables
- some fruits
Water
- Required by every cell to complete its process
- Many of body’s chem. reactions happen in water
- dehydration: lack of enough water in body
What are calories?
- calorie: amount of energy required to raise temp. of 1 g water by 1 °C
- dietary calorie (C.): equal to 1,000 calories
- calories often used to refer to C.
- Calories of nutrients
- Fat: ~9 C. / g
- Carbs and proteins: ~4 C. / g
- More C-H bonds in fats than carbs / proteins
- Calories needed for basic maintenance + active lifestyle
- 2,200 calories for female teens
- 2,500 calories for male teens
Beneficial Foods
- nutraceutical: substance purified from foods and taken as medicine to give health benefits incl. disease prevention
- functional food: food that has health benefits incl. disease prevention beyond nutritional benfit
- probiotics: foods that contain substances that help promote growth of helpful intestinal bacteria
Fitness
- 2 classes: cardiovascular and muscular
- Cardiovascular fitness delivers greatest benefits
- Heart rate may indicate level of fitness
- Benefits
- loss of excess weight
- lower blood lipids
- lower BP (blood pressure)
- increased energy lvls.
Diets and Dietary Supplements
- Balance of food types must be maintained
- Vegetarians avoid meat and fish on moral or ethical grounds
- Vegans do not consume any animal products
- Diets must be specially planned to incorporate all dietary nutrients
- Vitamins and supplements may be required if diet is lacking in certain nutrients
- A balanced diet will usually not require the use of vitamins
Drugs and Other Toxins
- psychoactive drugs: drugs that affect central nervous sys. and interfere w/ normal functioning of brain
- LD50: lethal dose for 50% of test pop.
Nicotine
- Found in tobacco and its products
- Extremely toxic
- Increases pulse rate and BP
- Interferes with vit. C absorption → impairs immune response
- Tobacco smoking may result in…
- hardening of arteries
- respiratory infections
- emphysema
- ulcers
- cancer
Caffeine
- Found in many plants incl. coffee and tea
- Toxic
- Acts as a diuretic (dilutes urine)
- Increases BP
- Constricts blood vessels
Alcohol
- Produced by yeast fermentation
- ORL-RAT LD50 7060mg/kg
- Excessive use problems:
- physical
- psychological
- social problems
LSD
- LSD: D-lysergic acid diethylamide
- Illegal hallucinogen
- IVN-RAT LD50 16 mg/kg
Heroin
- Derived from opium poppy Papaver somniferum
- Highly addictive illegal narcotic
- Lethal dose varies among individuals
- Users have greater tolerance to the drug
- Injected intravenously
- Intense rush
- Users prone to…
- liver disease
- infections
- collapsed veins
- hepatitis and HIV infection
Ecstasy
- Both a stimulant and hallucinogen
- Illegal neurotoxin
- Increases body temp, and
- Blocks serotonin uptake
- causing insomnia, and
- insensitivity to pain
Anabolic Steroids
- Synthetic derivatives of the male hormone testosterone
- Builds muscle tissue in patients
- Used illegally by athletes to boost performance
- Side effects
- liver damage
- heart problems
- high blood pressure
- mood swings
- female masculinization
