C4.1 - Genetic Continuity
Historical Information
- Since ancient times, people have recognized that certain traits are passed down along family lines
- A trait is any characteristic that can be passed or inherited from parent to offspring
Genetics in Prehistory
People have been experimenting in genetics for tens of thousands of years
The First Genetic Experiment
- Domestication of the family dog, Canis familiaris
- Mankind’s oldest and best friend
- Over thousands of years, certain traits such as temperament and body size were selected for
Agricultural Crops
Humans domesticate crops such as:
- barley
- wheat
- rice
- corn
- started agricultural revolution
Early Views of Inheritance
Aristotle (384-322 BC)

- Pangenes in blood contain a memory of each structure of human body
- “Bloodlines”
- “Blood relative”
William Harvey (1578-1657)

Human embryos form in stages like any other animal such as frogs or fish
Anton van Leeuwenhoek (1632-1723)

- Observed human semen
- Thought they represented preformed embryos
- Father of microscopy
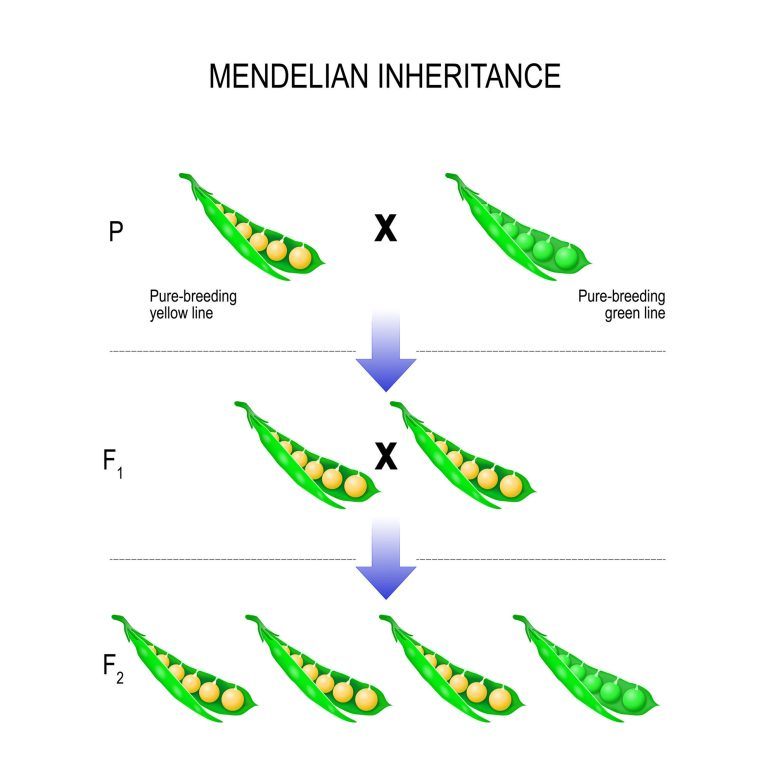
Gregor Mendel (1822-1884)

- Christian monk
- Experimented w/ pea plants
- Proposed theory of particulate inheritance
- modern concept of the gene
- Traits are determined by discrete units that are inherited intact through the generations
Modern Genetics
DNA discovered to be the molecule responsible for genetic information in 1950s
Biotechnology
- Human Genome Project complete sequence for entire human genome
- Has allowed rapid advancement in medicine, agriculture