C4.3 - Human Genetics & DNA
Introduction
- Mendel’s Laws also apply to humans
- Inheritance in humans is a challenge to reconstruct
- Mutations in human DNA result in defective proteins
- Mutation may be
- useful — positive mutation
- harmful — negative mutation
- with no effect — neutral mutation
The Genetic Material
deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA): molecule that composes genetic material
Packaging of DNA
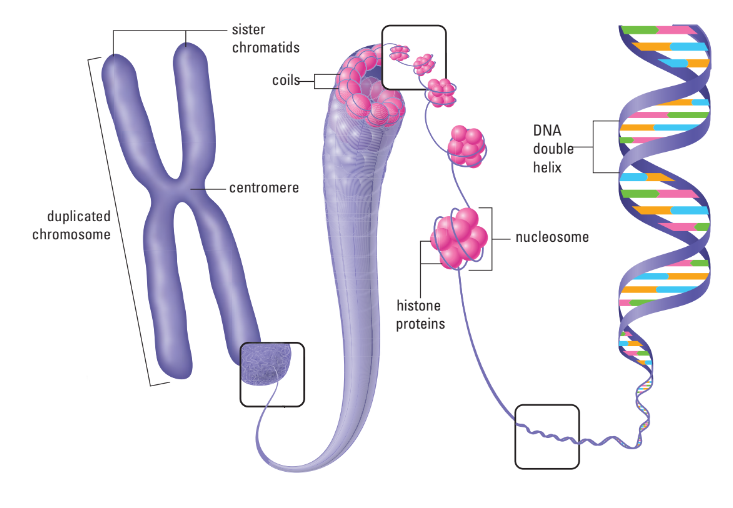
- chromatin: mass of long fibers of DNA and protein (not usually visible w/ light microscope)
- chromosome: condensed DNA molecule that is visible under light microscope
- 46 chromosomes in humans
- 78 chromosomes in dogs
- DNA tightly coiled around proteins called histones
- The DNA and histone packages form structures resembling beads, called nucleosomes
Structure of DNA
- 1950s: Rosalind Franklin used X-ray crystallography to study DNA
- She found DNA had a helical shape
- Watson and Crick used her data to model DNA as a double helix
- Their model had sugar-phosphate backbones outside, nitrogenous bases inside
Components of Model
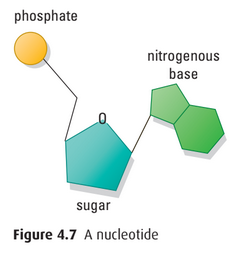
- DNA consists of long chain of subunits called nucleotides
- Parts of nucleotides
- deoxyribose: ring-shaped sugar
- phosphate group
- nitrogenous base: single / double ring of carbon and nitrogen atoms
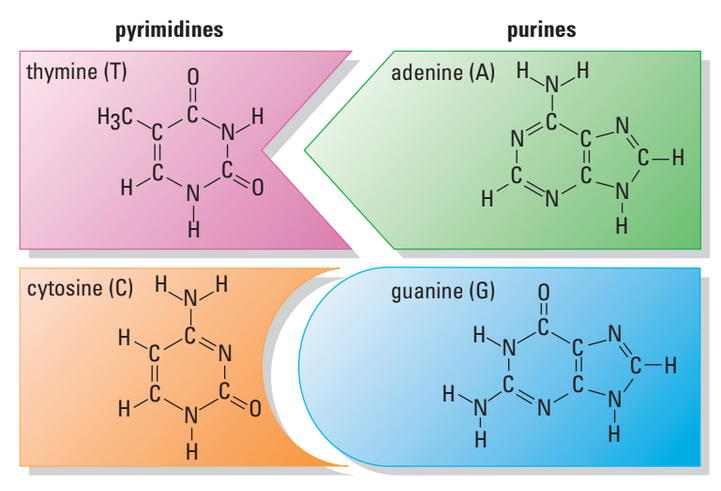
- 4 Types of Nucleotides
- differ only in their nitrogenous bases
- pyrimidines: single-ring structures
- thymine (T) and cytosine (C)
- purines: larger, double-ring structures
- adenine (A) and guanine (G)
- Molecular arrangement
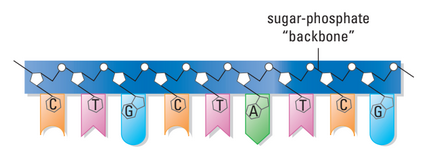
- Nucleotides are linked by covalent bonds between sugar and phosphate
- sugar-phosphate backbone: repeating pattern of sugar-phosphate
- base pair: bonds between specific nucleotides to hold them together
- complementary bases: nucleotides that hold each other
- A pairs to T
- C pairs to G
- hold DNA together
- causes the DNA to twist into a double helix
- Knowing one strand’s sequence lets you determine the other
- This explains how DNA is copied and passed on
DNA Sequences
- nucleotides can form countless sequences of varying lengths
- sequences store genetic information that codes for proteins and cell functions
DNA strand
Autosomal Recessive Inheritance
- autosomal recessive inheritance: recessive (masked) alleles carried on autosomes, not sex chromosomes
- autosomes: non-sex chromosomes, usually numbered
- harmful recessive mutations may persist masked by dominant trait
- i.e. Tay-Sachs disease
- individuals lack lipid-degrading enzyme, fatal
- i.e. Albinism
- eyes, skin, hair lack pigment melanin
- individuals lack melanin-producing enzymes
Codominant Inheritance
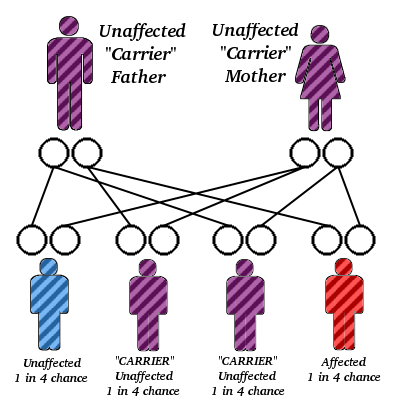
codominant inheritance: form of inheritance where two different forms of an allele are expressed equally
Sickle-Cell Anemia
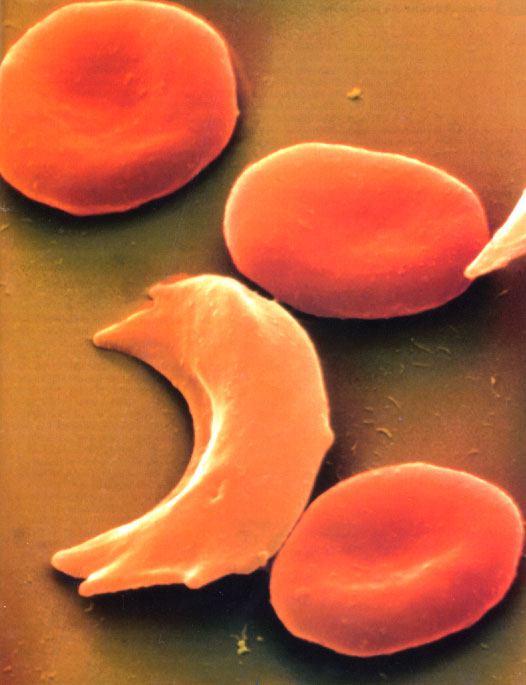
- individuals have hemoglobin defect
- hemoglobin: oxygen-carrying molecule in RBCs
- RBCs malformed and are prone to clogging capillaries starving tissues of oxygen
- HbA HbA: normal, RBCs often never sickle
- HbS HbS: severe, often fatal anemia, RBCs have sickle shape
- HbA HbS: no anemia; RBCs sickle only under low-oxygen conditions
- recessive gene may give heterozygous advantage to carriers
- disorder found more frequently in African malarial zones
Autosomal Dominant Inheritance
- autosomal dominant inheritance: dominant alleles carried on autosomes
- result from chance mutations;
- or symptoms arise after child-bearing age
- i.e. Huntington’s Disease
- deterioration of brain tissue
- symptoms appear after age 35
- genetic test available
Incomplete Dominance
- incomplete dominance: phenotype midway between dominant and recessive
- i.e. hypercholesterolemia
- individuals lack LDL receptor protein
- results in high cholesterol levels
- Incomplete Dominance = Codominance?
Sex-Linked Recessive Inheritance
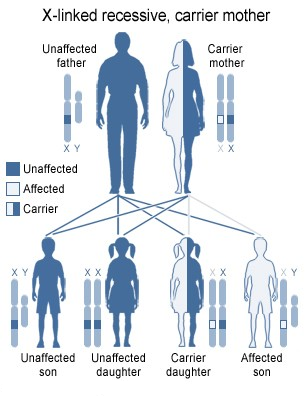
- sex-linked recessive inheritance: recessive alleles carried over through sex chromosomes
- sex chromosomes: chromosomes that determine an individual’s sex
- first discovered by Morgan in fruit flies
- trait carried mostly on X chromosome, seldom on Y
- much more prevalent in male populations
- crosses can be visualized with Punnet squares
i.e. Colorblindness
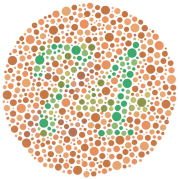
Ishihara colorblind test
- affects 8% of men and 0.04% of women
- alleles for red and green found on X, but red is defective
- colorblind men cannot distinguish between red and green
i.e. Hemophilia
- hemophilia: blood clotting disorder
- individuals lack clotting factors
- 3 forms
- A — Factor XIII
- B — Factor IX
- C — Factor XI
- mild cuts or bruises may lead to extreme joint pain or death
- treated w/ injection of clotting factors
- tainted blood scandal
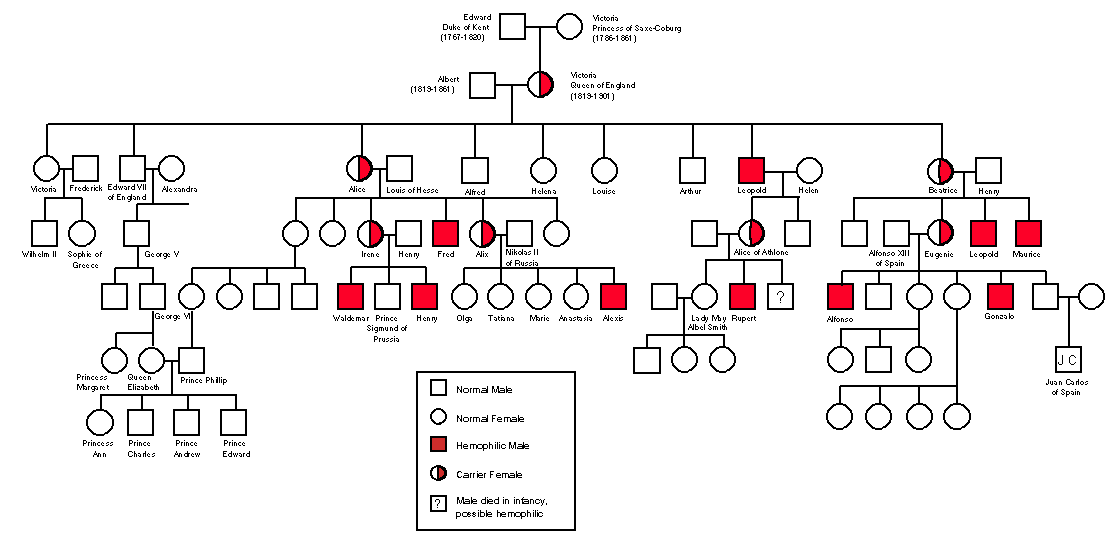
- studied in pedigree of Queen Victoria’s family
Queen Victoria’s Family Tree
Genetic Testing
- carrier testing: test to determine if an individual carries a copy of a mutation that his / her children could inherit
- presymptomaticing: test that predicts the likelihood of developing a genetic condition
- i.e. looking at family history
- diagnostic genetic testing: tests that confirms a diagnosis when symptoms for a particular genetic condition are present
Prenatal Testing
- human embryo becomes fetus ~7 weeks after fertilization
- prenatal testing: test that detects small-scale mutations or chromosomal alterations in a fetus
- conditions often screened for
- spina bifida: birth defect involving incomplete development of spinal cord
- may result in protrusion from opening in spine
- Down syndrome
- spina bifida: birth defect involving incomplete development of spinal cord
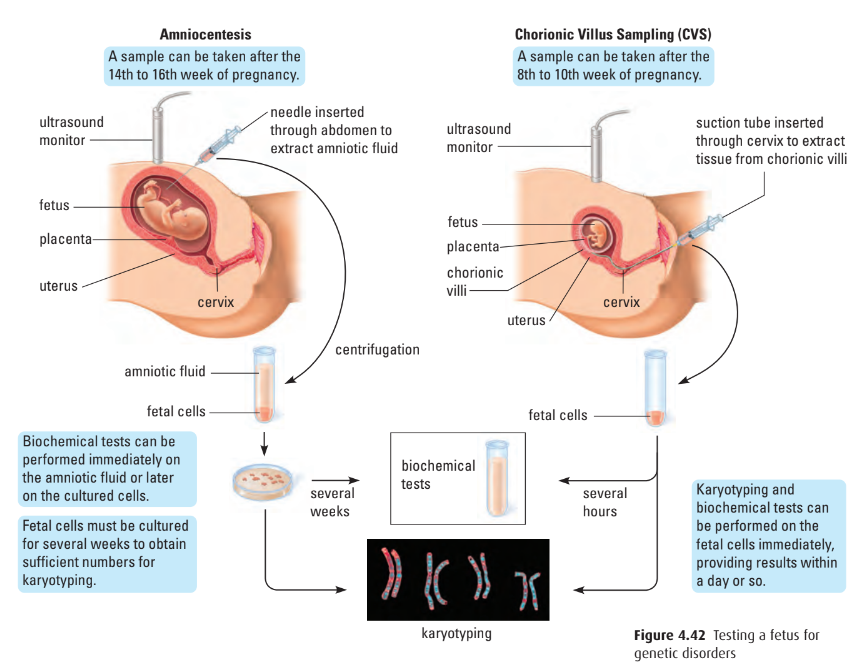
- amniocentesis: prenatal screening performed between 14th to 20th week of pregnancy (from textbook)
- physician inserts needle into mother’s uterus
- extracts some of amniotic fluid surrounding developing fetus
- fetal cells tested for genetic disorders
- chorionic villus sampling (CVS): fetal testing of chorionic villi
- chorionic villi: fingerlike projections that protrude from tissue surrounding fetus
- physician extracts small sample of chorionic villi
- by inserting narrow, flexible tube into mother’s uterus
- conducted as early as 8th week of pregnancy
- Risks of Complication
- maternal bleeding
- miscarriage
- premature birth
- usually conducted only if there is high risk of genetic disorder
Newborn Screening
- newborn screening: testing a newborn infant for genetic disorders
- can detect some genetic disorders at birth through simple tests performed in hospitals
- screened for phenylketonuria (PKU)
- inherited disorder
- inability to break down naturally occurring amino acid phenylalanine
- accumulation of phenylalanine may lead to severe developmental delays
- diet low in phenylalanine usually sufficient to prevent onset of developmental delays